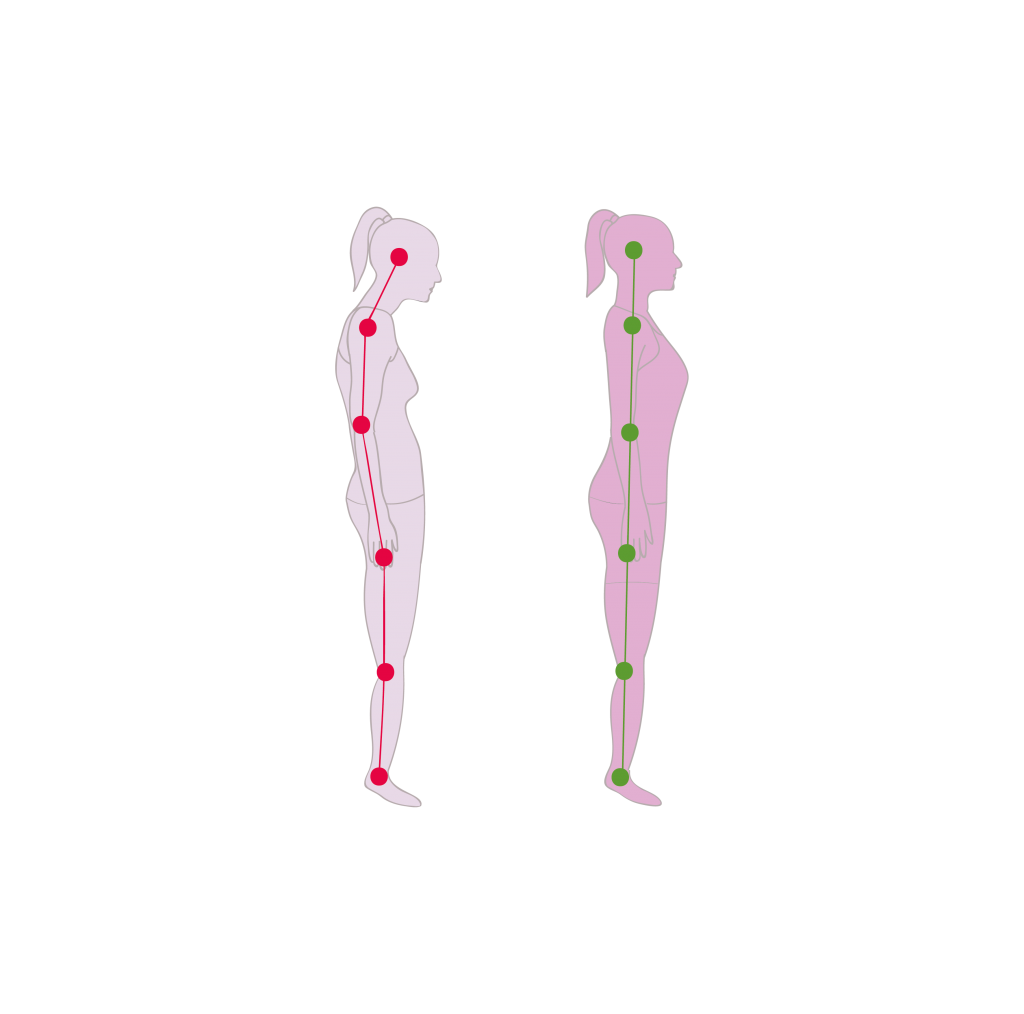IMPACTS
In our mouth, the teeth are placed at the balance of forces between the tongue on one side, the lips and the cheeks on the other. When the tongue dysfunctions or is incorrectly placed, the balance of forces is disrupted. It is this imbalance that causes some of the dental disorders presented below.
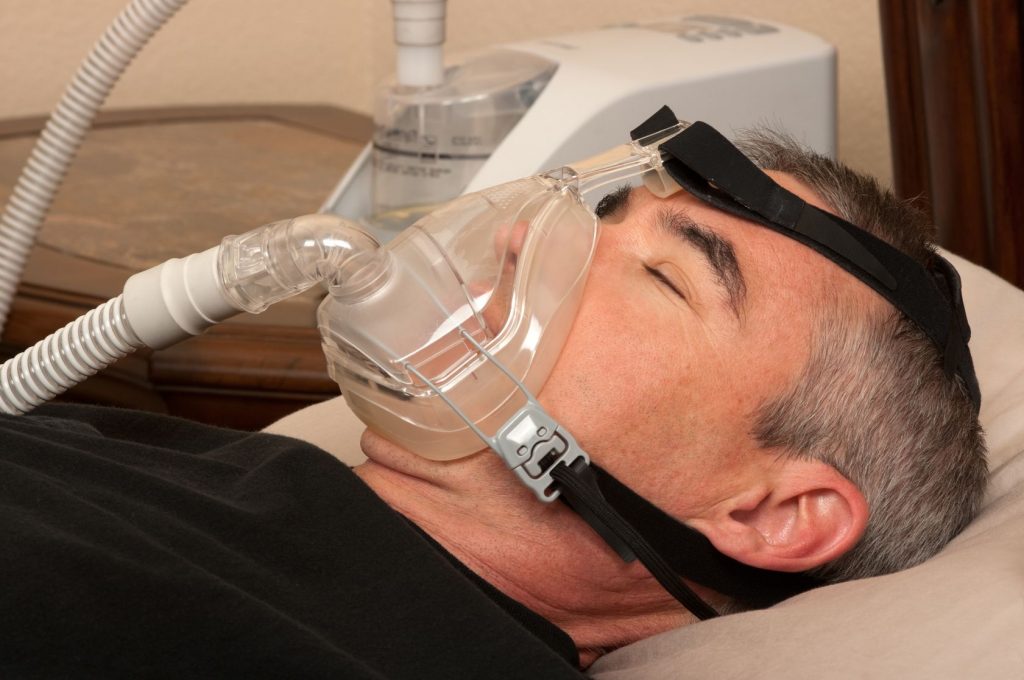
The tongue is also at the crossroads of the so-called “upper” airways. Its dysfunctions or mispositions can also disturb the passage of air: oral breathing, ENT pathologies, snoring or Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome (OSA).
Beyond that, it has been found that tongue is also involved in some posture disorders.
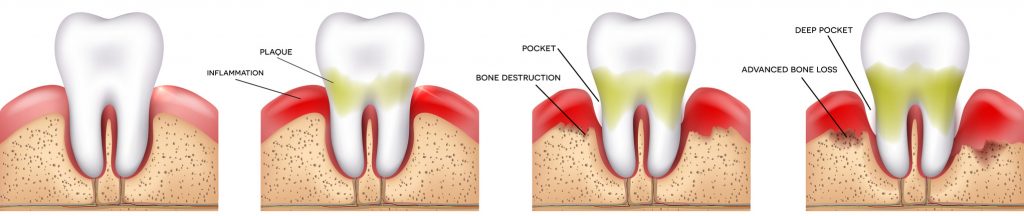
DENTAL TROUBLES
In our mouth, teeth position is a results of a balance of forces between tongue on one side, lips and cheeks on the other side. When the tongue malfunctions or does not position itself correctly, the balance of forces is disturbed. This imbalance causes some of the dental disorders listed below. The tongue is also at the crossroads of the "upper" airways. Its dysfunctions or malpositions can also disturb passage of air: mouth breathing, snoring or Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome (OSA). Beyond that, it has been found that tongue is also involved in some posture disorders.MOUTH BREATHING
Physiological breathing is nasal breathing. According to several studies, oral breathing affects nearly 55% of the population. Only in 20% of cases is it due to a deformation of the nasal septum, for example because of an accident. In the remaining 80% of cases, it could be the consequences of a tongue dysfunction. This type of breathing can cause many disorders, such as craniofacial morphology troubles, infections, postural disorders, or affect the neurological or cardiovascular system. However, it especially alters our concentration, our vigilance, our cognitive sense in daily life.